SFP, or Small Form Factor Pluggable Transceiver, is a compact, hot-swappable network module. From data centers to home networks, from large enterprises to small offices, SFPs have become a key component in ensuring data mobility and network interconnection. Its role in modern communication and data centers cannot be ignored, it simplifies the complexity of the network, provides greater flexibility, and promotes the development of network technology.

Originated in the late 1990s, the predecessor of SFP was GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter). As technology evolves, network devices require smaller, more compact interfaces, which makes SFP an ideal choice. GBIC, due to its relatively large size, is gradually replaced by miniaturized SFP. Compared with GBIC, SFP provides a smaller size, which means more ports can be accommodated in the same size switch or router.
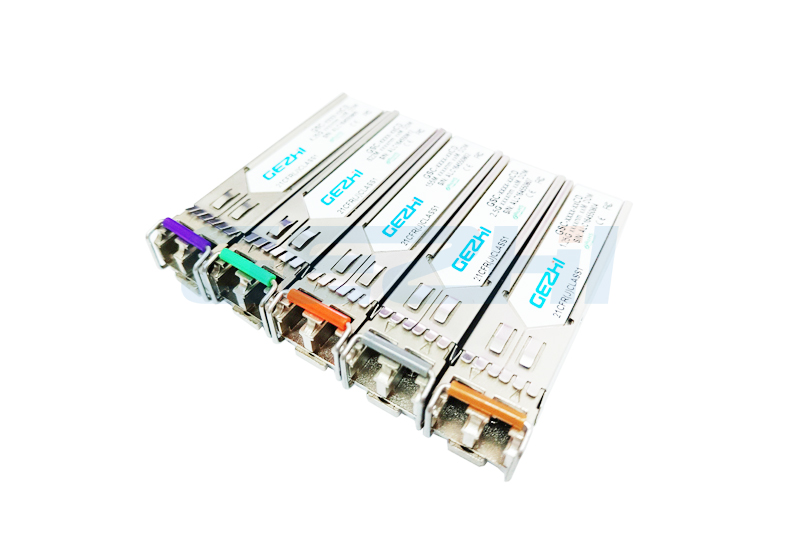
SFP modules consist of several components. Its main feature is its compact size, typically 8.5mm x 13.4mm x 56.5mm.
Physical Construction: Modules are usually made of metal or plastic and have a slot for insertion into the corresponding SFP port. One end of the module has a set of electrical contacts that transfer data and power. On the other end is an interface, which can be a fiber optic connection or a copper wire connection.
Working principle: The SFP module receives and transmits data. For fiber optic SFP, it contains a laser to convert the electrical signal to optical signal and transmit it through the fiber optic line. A photodetector at the receiving end converts the light signal back into an electrical signal.
SFP's diversity is a key factor in its success. According to different needs and applications, there are many kinds of SFP modules on the market.
Basic SFP module:
Fiber SFP: This is the most common type and is used for long-distance data transmission. It can be single-mode or multi-mode, depending on the transmission distance. Single-mode SFPs are typically used for transmissions over 10km, while multimode is used for shorter distances.
Copper SFP: Designed for short-distance data transmission, such as connections in the same computer room. It uses standard copper wire technology such as twisted pair.
SFP+ (Enhanced Small Form-factor Pluggable):
As the demand for data transmission grows, SFP technology has undergone further innovation and upgrades. SFP+ came into being, providing a rate of 10Gbps, which is an enhanced version of the original SFP.
10GBASE-SR: For short-distance applications, usually used inside data centers, using multimode fiber, the maximum transmission distance can reach 300 meters.
10GBASE-LR: Designed for long-distance applications, using single-mode fiber, the maximum transmission distance can reach 10 kilometers.
10GBASE-ER: Suitable for ultra-long-distance applications, using single-mode fiber, the maximum transmission distance can reach 40 kilometers.

SFP28:
With the emergence of 25G Ethernet, SFP28, as a 25Gbps rate module, has become a new standard for data centers. It inherits the form factor of SFP+, but provides a higher transmission rate.

BiDi SFP:
BiDi SFP modules use bi-directional transmission technology, allowing bi-directional communication over a single optical fiber. This reduces the use of fiber optics and at the same time lowers the cost of cabling. By using two different wavelengths of light, BiDi SFPs can transmit and receive on the same fiber.

CWDM and DWDM SFPs:
Wavelength division multiplexing technology is an important direction of optical fiber communication, which allows signals of multiple wavelengths to be transmitted on a single optical fiber, thus greatly increasing the transmission capacity.
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing): Provides 8 to 16 different wavelengths for connections between cities and regions.
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing): Provides more wavelength options, making it ideal for long-haul and ultra-long-haul applications.

Compact SFP (cSFP):
cSFP is an innovative design capable of accommodating two independent channels in a single SFP port. This not only saves physical space, but also increases port density, making network design more economical and efficient.
SFP technology has been widely used in many industries and scenarios due to its flexibility and scalability. The following are some major application areas:
Data Center: With the rise of cloud computing, big data and artificial intelligence, the data center has become the core of modern IT infrastructure. SFP and its variants such as SFP+ and SFP28 play a key role in these facilities, ensuring high-speed, reliable data transmission.
Telecommunications: To meet the demands of global Internet users, telecommunications companies must ensure that their networks are high-capacity and highly reliable. DWDM and CWDM SFP modules allow these companies to add capacity on existing fiber optic networks without adding new physical lines.
Enterprise Networks: Enterprise networks require stable, high-speed, and secure connections. SFP technology allows these organizations to easily expand their networks as needed, whether within the office or connecting to remote branch offices.
Medical field: Modern hospitals and clinics rely on high-resolution medical images and real-time data streams, such as patient monitoring systems. SFP modules ensure that these critical data can be transmitted quickly and accurately.

Case 1: High-speed data link between cities
The challenge for a major telecommunications company was to provide a high-speed data link between two major cities without incurring additional infrastructure costs. The company chose to use DWDM SFP modules, which allowed them to add up to 40 different data lanes to a single existing fiber optic line. As a result, the company managed to increase the transfer rate and provide a higher quality of service to its customers.
Case 2: Expansion of a large data center
A cloud service provider was looking for ways to expand the capacity of its data center. Using SFP28 modules, they are able to provide a connection speed of 25Gbps, which means higher data throughput and lower latency. With this upgrade, they not only improved their service quality, but were also able to support more customers.

SFP technology and its associated modules provide a powerful and flexible solution for modern communications and data transmission. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect these modules to become more advanced in the future, opening up more possibilities for various industries and applications.
 Next-Gen Networking Solutions | SFP Modules, Trans...
Next-Gen Networking Solutions | SFP Modules, Trans...
 High-Speed 40G QSFP+ Optical Transceivers for Long...
High-Speed 40G QSFP+ Optical Transceivers for Long...
 400G QSFP-DD Optical Modules: High-Speed Network C...
400G QSFP-DD Optical Modules: High-Speed Network C...
 10G SFP+ Cables - Reliable High-Speed Connectivity...
10G SFP+ Cables - Reliable High-Speed Connectivity...
 10GBASE-T SFP+ Copper Transceiver - High-Speed Dat...
10GBASE-T SFP+ Copper Transceiver - High-Speed Dat...
 High-Speed 10Gbps CWDM SFP+ Optical Transceiver - ...
High-Speed 10Gbps CWDM SFP+ Optical Transceiver - ...
 1.25Gbps BiDi SFP Transceivers: Revolutionizing Ne...
1.25Gbps BiDi SFP Transceivers: Revolutionizing Ne...
 1G SFP Module: High-Speed Fiber Transmission
1G SFP Module: High-Speed Fiber Transmission
 40G QSFP+ SR4: High-Speed Short-Distance Data Conn...
40G QSFP+ SR4: High-Speed Short-Distance Data Conn...
 100G QSFP28: High-Speed Optical Transceiver
100G QSFP28: High-Speed Optical Transceiver
 400G QSFP-DD: High-Speed Data Revolution!
400G QSFP-DD: High-Speed Data Revolution!
 In-Depth Analysis of SFP Modules: History, Working...
In-Depth Analysis of SFP Modules: History, Working...
 Comprehensive Guide to SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, an...
Comprehensive Guide to SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, an...
 SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+ and QSFP28 optical modules
SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+ and QSFP28 optical modules
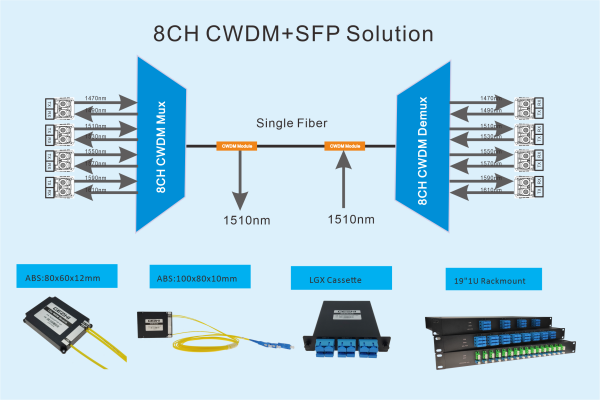 CWDM Passive System with SFP
CWDM Passive System with SFP