An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a critical piece of hardware that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. This power protection system offers near-instantaneous protection from power interruptions. To fully grasp the essence and function of a UPS, it's crucial to understand its three general categories: Offline UPS, Online UPS, and Line-Interactive UPS. Each type comes with its unique working principles, functions, advantages, and disadvantages, thus offering different levels of power protection.
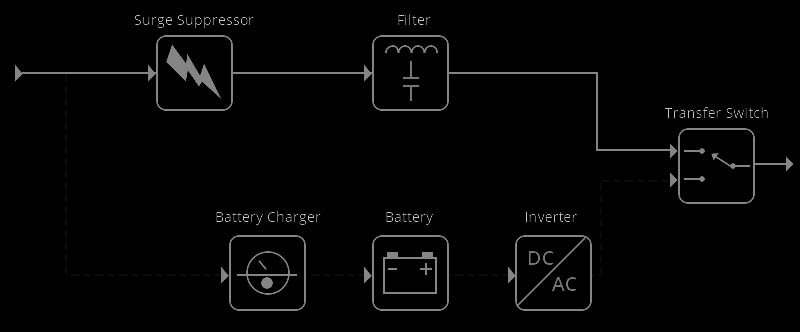
These three types of UPS systems—Offline, Online, and Line-Interactive—are distinguished by their individual working principles. Each method represents a different approach to provide emergency power during a power failure. Let's delve into the working principles of each UPS type.
An Offline UPS, also known as Standby UPS, offers basic power protection. During normal operation, an Offline UPS allows power to pass straight through from the input source to the connected devices. Its energy storage components remain offline, with the battery charger and battery staying connected to the mains power to ensure that the battery is always fully charged. The inverter only switches on when a power failure is detected. At that point, the UPS switches the load to the battery, which provides power to the inverter, allowing it to supply power to the connected devices.
A Line-Interactive UPS offers a more sophisticated level of power protection. Unlike an Offline UPS, the inverter in a Line-Interactive UPS is always connected to the output, which enables it to respond more quickly to a power outage. When power is lost, the UPS reroutes the DC path from the battery to supply power to the inverter, avoiding the switch-over delay that occurs with an Offline UPS. This provides an uninterrupted power supply to the connected devices.
An Online UPS, also known as a Double Conversion UPS, offers the highest level of power protection. It continuously converts incoming AC power into DC power, and then back into clean, stable AC power for the connected devices. The battery is always connected to the inverter, so there is no power interruption during a failure. As a result, connected devices continue to receive steady, uninterrupted power even when the mains power is experiencing issues.
All three UPS systems are designed to protect equipment and maintain power during power interruptions. However, their varying working principles lead to differences in their capabilities.
While being the most basic type of UPS, an Offline UPS still offers valuable power protection, especially for less critical applications. It is typically used in environments where power supply is relatively stable, and power failures are infrequent.
Cost-effective: An Offline UPS is usually the least expensive option.
Efficient operation: During normal operation, there is little to no energy loss.
Limited power protection: An Offline UPS only provides power protection when a power failure is detected. It does not correct minor power fluctuations or disturbances.
Switch-over time: There is a brief interruption in power (typically a few milliseconds) when the UPS switches from mains power to battery power during a power outage.
A Line-Interactive UPS offers an improved level of power protection over an Offline UPS and is typically used in environments where power supply is relatively unstable.
Improved power protection: In addition to providing power during an outage, a Line-Interactive UPS also offers voltage regulation to correct minor power fluctuations without switching to battery power.
Fast switch-over time: Thanks to its always-connected inverter, a Line-Interactive UPS can switch to battery power almost instantly during a power outage.
Still some power interruption: Despite its fast switch-over time, a Line-Interactive UPS still has a brief power interruption during the switch-over process.
Dependence on battery: A Line-Interactive UPS relies heavily on its battery and can therefore be affected by battery performance.
An Online UPS offers the highest level of power protection and is typically used in environments where constant, high-quality power is required.
Superior power protection: An Online UPS offers constant, clean, high-quality power, regardless of the condition of incoming power.
No switch-over time: Since it is always connected to the inverter, an Online UPS does not experience any power interruption during a power failure.
Cost: An Online UPS is usually more expensive than an Offline or Line-Interactive UPS.
Efficiency: Due to its constant double conversion process, an Online UPS may be less energy-efficient than other types of UPS.
The type of UPS required depends on the specific requirements of the equipment, the environment, and the level of power protection needed.
Below are some typical applications for each type of UPS:
Offline UPS are commonly used in home offices, POS systems, and other low-risk environments where brief power interruptions are acceptable.
Line-Interactive UPS are often used in small to medium-sized businesses, server rooms, and network equipment where a higher level of power protection is needed and minor power fluctuations are common.
Online UPS are typically used in critical infrastructure, such as data centers, medical facilities, and industrial environments, where constant, high-quality power is required and any interruption in power could have serious consequences.
To choose the right UPS, you should consider the following factors:
Power needs: The total power requirements of your equipment.
Level of protection required: The sensitivity of your equipment to power fluctuations and interruptions.
Cost: Your budget and the potential cost of power interruptions.
Environment: The quality and reliability of your power supply.
Remember, the goal is to find a balance between cost and the level of power protection required. You may also want to consult with a power protection specialist or UPS vendor to help you make the best decision.