PCI Express (PCIe) has been a game-changer in the field of networking, offering higher bandwidth, greater flexibility, and enhanced performance. In this comprehensive guide, we dive into the intricacies of PCIe cards, explore their different types, understand the meanings behind terms like PCIe x8 or PCIe x16, and guide you in finding the best PCI Express card for your needs.
PCI Express, or PCIe, was developed to meet the escalating demands for higher bandwidth and better performance in networking devices. Over the years, it has become a widely adopted standard for various network devices, especially the PCIe card. A PCIe card, also known as a PCI Express card or PCIe-based card, is a type of network adapter with a PCIe interface. It's used in motherboard-level connections as an expansion card interface. Specifically, PCIe-based expansion cards are designed to fit into PCIe slots in the motherboards of hosts, servers, and network switches. Modern PCs usually come with dedicated PCIe slots that accommodate these cards. Comparisons are often drawn among PCI, PCI-X, and PCI-E – the three versions of network adapters. However, the latest trend clearly leans toward the PCIe card, given its superior design and topology.
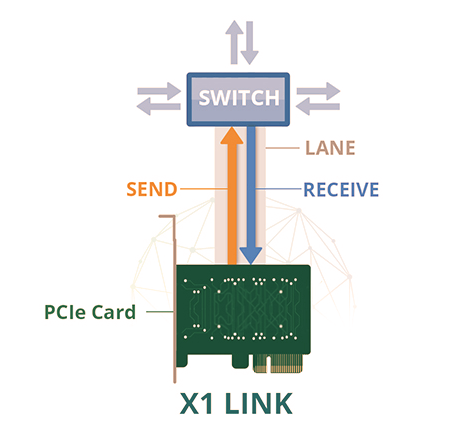
Unlike a traditional bus that handles data from multiple sources, a PCIe card establishes point-to-point connections through switches. This setup allows precise control over where the data needs to go. Once a PCIe card is inserted, a logical connection - termed an interconnect or link - is formed between the slot and the card, enabling a two-way communication channel. Each PCIe slot contains one or more lanes, and each lane is composed of two different data-transferring pairs – one for transmitting and the other for receiving data. Thus, each lane consists of four wires or signal traces.
PCIe cards can be categorized based on their sizes and their versions. These distinctions are crucial in understanding their compatibility and functionality.
The size of a PCIe card is often denoted by the number of lanes it possesses. The most common sizes are x1, x4, x8, and x16. There is also an ultra-rare x32 size, which comes with a maximum of 32 lanes. The "x" is followed by a number indicating the number of lanes in the PCIe slot. For instance, a PCIe x4 card would have four lanes.
| PCIe Slot Width | Number of Pins | Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| PCIe x1 | 18 | 25 |
| PCIe x4 | 21 | 39 |
| PCIe x8 | 49 | 56 |
| PCIe x16 | 82 | 89 |
PCIe 1.0 was initially launched in 2003, and to meet the growing demands for higher bandwidth, subsequent versions including PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, and PCIe 5.0 were introduced. A future version, PCIe 6.0, is anticipated in the near future.
| Version | Introduced | Transfer rate (x1) | Transfer rate (x16) | Line code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe 1.0 | 2003 | 2.5 GT/s (250 MB/s) | 40 GT/s (4.0 GB/s) | 8b/10b |
| PCIe 2.0 | 2007 | 5.0 GT/s (500 MB/s) | 80 GT/s (8.0 GB/s) | 8b/10b |
| PCIe 3.0 | 2010 | 8.0 GT/s (984.6 MB/s) | 128 GT/s (15.75 GB/s) | 128b/130b |
| PCIe 4.0 | 2017 | 16.0 GT/s (1969 MB/s) | 256 GT/s (31.51 GB/s) | 128b/130b |
| PCIe 5.0 | 2019 | 32.0 GT/s (3938 MB/s) | 512 GT/s (63.02 GB/s) | 128b/130b |
Choosing the correct PCIe card depends on several key factors:
PCIe Card Version and Slot Width: It's vital to ensure that the PCIe card version and type are compatible with your current equipment and network environment.
Protocol Standard: Depending on your needs, you may require the card to support standards such as RDMA, RoCE, iSCSI, and FCoE.
Controller: Chipsets from reputable manufacturers like Intel, Broadcom, Mellanox, and Realtek are preferable.
Additionally, consider other influencing factors such as transmission speed, port number, connector type, operating system, brand, and price.
As high-end software evolves to meet growing demands, PCIe performance continues to break new ground. The ongoing development of PCIe cards like PCIe 4.x, PCIe 5.x, and the upcoming PCIe 6.x demonstrates the potential of the PCIe standard in bridging the gap between PCIe-based cards and hosts.
Click here to explore more about PCIe cards.